For example, last year, the annual report noted that the government was sitting on a report of the minimum wage commission (struck in 2019, reporting in early 2020), The expectation was that this report recommended expanding the existing two-tiered minimum wage and that the government would use this as a pretext for reimplementing a lower wage for some servers.
That report was never released (as far as I can tell). This year, there is literally no mention of the minimum wage. Perhaps the government has given up on the idea given the struggle faced by employers to recruit servers? This, in turn, suggests that the existing minimum wage (stagnant since 2018) may be inadequate.
Or maybe, with three Labour ministers in a year, each worse than the last, the department just lost track of this issue? Anyhow, let's have a look at the various regulatory areas the government reports on.
Employment Standards
Employment standards set out the minimum terms and conditions of work. If your employer screws you, you can file a complaint. Over time, complaint numbers have dropped significantly.
There is, once again, no concrete explanation for this drop. Many things can affect complaint volume, including the number of workers and their expectation that complaining will be beneficial (e.g., result in a net gain, not result in retaliation). A 41.9% reduction in complaints since 2016/17 is pretty significant, especially since employment numbers rebounded during 2021/22.
Overall inquiries by Albertans about Employment Standards are also down. There were 131,189 phone and email inquiries in 2019/20 and only 70,826 in 20221/22 (a 46.0% reduction). Again, no compelling explanation for this change is offered. One possibility is that Alberta workers are decreasingly seeing Employment Standards as a viable way to enforce their rights. The drop since the UCP came to power is particularly striking.
There was an increase in Employment Standards enforcement this year. Instead of one administrative penalty, Alberta issued three penalties, the largest being $1500. The lack of consequences for noncompliance (beyond maybe having to pay some or all of what an employer should have paid in the first place) not only makes Alberta’s Employment Standards laws pretty toothless, but, in fact, economically incentivizes employers to cheat workers because they will likely get away with it.
Occupational Health and Safety
Alberta’s OHS system is designed to reduce workplace injuries and fatalities by educating employers and workers about safe work practices, conducting inspections to ensure compliance, and issuing orders and penalties when employers fail to operate safely.
The bump in inspections in 2020/21 was due almost entirely to additional COVID-related inspections and numbers seem to have returned to historical numbers. Almost 12,000 inspections seems like a lot of inspections, but we need to consider the context.
There were about 155,000 employers registered with the WCB. That undercounts total employers but whatever—this is back of napkin work. If we use 155,000 as a rough proxy for total employers and there were 11,798 inspections, we’re (roughly speaking), looking at a workplace being inspected once every 13 years.
If you did something more fine-grained (e.g., bigger employer pool; controlled for employers getting inspected more than once in a year), that telescopes the inspection cycle out some (maybe once per 15 years, maybe longer). The point, though, is that most worksites will effectively never get inspected.
If workplaces do get inspected, what happens? Mostly likely, if there are violations found, employers just get ordered to remedy them. But the number of compliance orders has dropped by about half since 2018/19 (the last full year of the ND government).
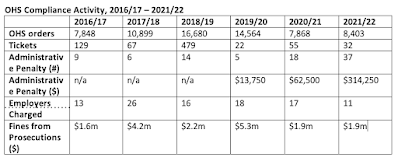
OHS almost never uses the enforcement tools available to it. OHS tickets dropped from 479 tickets in 2018/19 (again, the last year of the NDP government) to 32 this past year (a 93.4% drop). Of the 32 tickets issued in 2021/22, nine went to employers while the rest went to supervisors or workers. The largest ticket to an employer was $575 while the largest ticket to a worker was $230. These values have not changed in recent memory
Interestingly, the number and value of administrative penalties went up significantly this year, especially in dollar value. I don’t know what explains this. Only 11 charges were laid under the OHS Act, compared to 17 the previous year. Fines from prosecutions remained steady at $1.9m, with $1.2m being paid in the form of creative sentences (e.g., donations to community groups).
Effectiveness of Injury Prevention
So is this approach to injury prevention effective? One way to measure prevention effectiveness is to look at injury outcomes (particularly injury rates per 100 person-years worked) over time. Using a rate controls for fluctuations in the population over time and allow us to see patterns.
Alberta uses two main injury rates: lost-time claims and disabling injuries.
- Lost-time claims are accepted are injuries that required time off work beyond the date of injury. These are usually the most serious kinds of injuries.
- Disabling injuries are accepted injury claims that required time off or modified work duties.
The government notes that COVID played a significant role in rising disabling injury rates, If COVID-related claims are excluded, the DI rate would be 2.32 in 2020/21 and 2.46 in 2021/22.
Labour Relations
The Alberta Labour Relations Board (ALRB) administers and adjudicates applications and complaints about labour relations. The most interesting datapoint in the annual report is the number of certification applications (i.e., when a union applies to represent a group of workers).
In 2017, the ND government made it easier for workers to unionize by allowing card-check certification. Like every other jurisdiction where this change has been implemented, unionizing efforts increased significantly (because employers are deprived of the opportunity to meddle in the workers’ choice). In 2019, the UCP removed card check and, not surprisingly, certification dropped significantly. There are some confounding factors here (lag effects, COVID in 2020 and rising interest in unions in 2021) that we can’t control for, but that pattern is plain enough.
There are also a couple of interesting things tucked away in the details. There has been a dramatic increase in the number of days it takes for an application to get to hearing. This matters because delay usually benefits one side (almost always the employer).
The Board also continues to lag in rendering a decision in a timely manner. Again, delay tends to benefit employers.
This is partly explained as a function of writing time lost to additional administrative demands related to virtual hearings.
Conclusion
Overall, the administrative performance of Alberta’s labour law regime has declined over time, particularly since the UCP took office. Particularly worrying is the increase in injuries and the decline in certification applications. The underlying issue likely reflects policy directions and/or funding reductions enacted by the UCP.
No comments:
Post a Comment